
The metric units of measurement in mathematics are standard units defined to measure length, height, weight, area, and capacity ( volume). So, gradually better units of measurement were invented.Īs a result, the metric system, also known as the International System of Units (called the SI units - the modern form of the metric system), the Imperial system, and US customary units were standardized across the world as the units of measurement to get more accurate results. Since the body parts vary from person to person, these methods of measurement did not give very accurate results. For example, we used the body parts to measure the length such as hand span, foot span, arm span, cubit, pace, etc. In the early days, when we didn't have any proper tools to measure the physical quantities, we use some informal methods and units of measurement. These units of measurement have evolved since then and we have different systems of measurement now which are more convenient and easy to use. We have been using different units to measure these quantities like length, mass, volume, current, temperature, etc. The units of measurement are the collection of standard and other units that are used to measure various physical quantities. We shall solve various examples using the different units of measurement for a better understanding of the concept. Generally, we measure almost everything around us in our daily lives such as how many hours we have worked and slept, the amount of water we drink, our body weight, height, distance traveled on foot and by car.
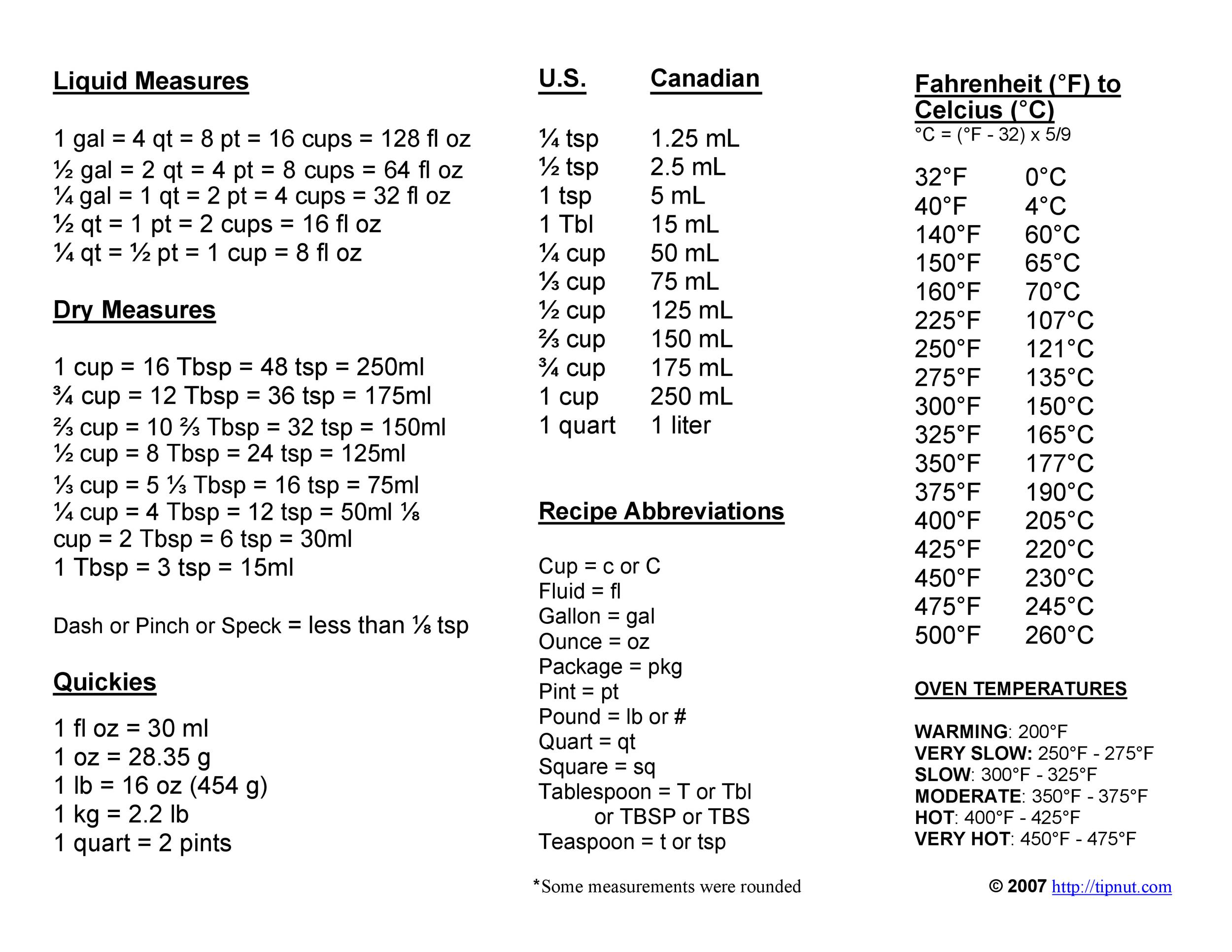
We will also discuss the various measurement units used for measuring length, mass, time, temperature, and volume. In this article, we shall explore the concept of metric and imperial units of measurement.
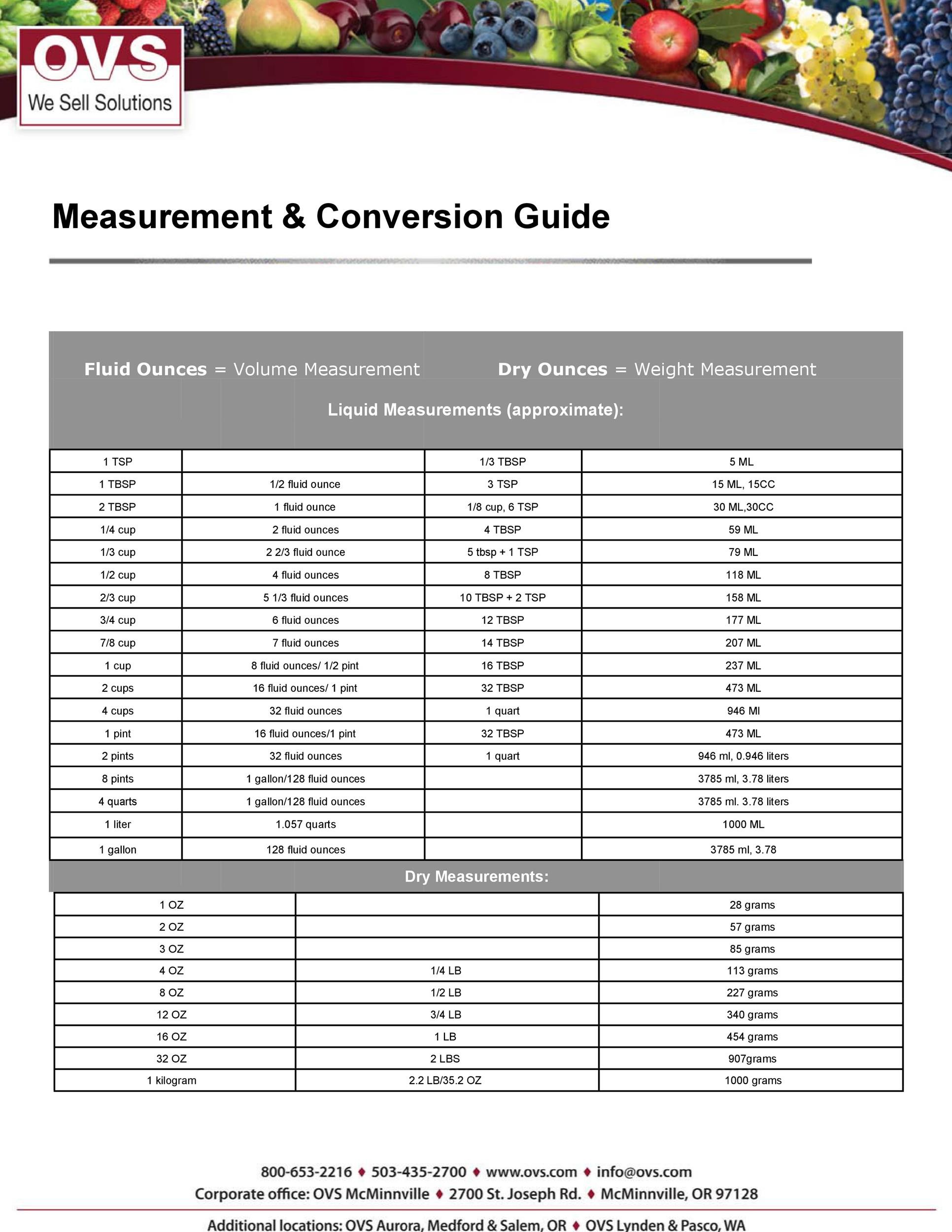
We use the measuring units to compare how large or small a physical quantity is as compared to the basic standard quantity. Units of measurement have also evolved and played a crucial role from the early ages till the present.
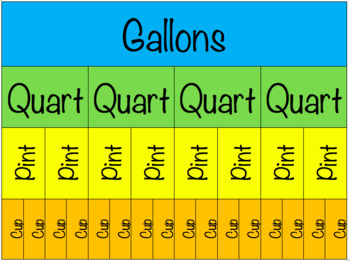
We use different measurement units to represent the magnitude of the physical quantities including the traditional units, the Metric System of units, the imperial system of units, and US customary units. The units of measurement are the units that are used to represent physical quantities like length, mass, temperature, current, area, volume, intensity, etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
