
Output of above command is as shown below (F: 5) So that it will merge the changes to my local forked develop branch. In my case, above command will be git merge upstream/develop. Execute the following command to merge these changes with our local fork repository.Ībove command will merge the changes that we pulled down in step 3 to local forked master branch.Output of above command is as shown below (F: 4) In above command, upstream is the same alias name that we have used while adding the original/upstream repository link in step 2. Execute the following command to pull down the changes from original/upstream repository on your local.After adding the remote repository link, execute git remote –v command again to make sure the original/upstream repository link is available in output. This is the same link that we use to clone this repository on our local machine. In my case original/upstream repository link is. Click on "Clone or download" button and copy the https web URL as shown below (F: 3) To get this URL, go to the original/upstream repository page on GitHub. We will be using this alias name to pull down the changes from original/upstream repository.Īlso, replace the link in the above command with original/upstream repository link of your forked repository.

In the above command, the word upstream is like an alias for that URL, so that we can easily access it. If your output only contains your forked repository link (origin), then we can add the original/upstream repository link using the following command. In the above image, origin points to my fork repository and nopSolutions are upstream points to original/upstream repository. Output of the above command is as shown below (F: 2). To do this, execute the following command to get the list of all tracked repositories.
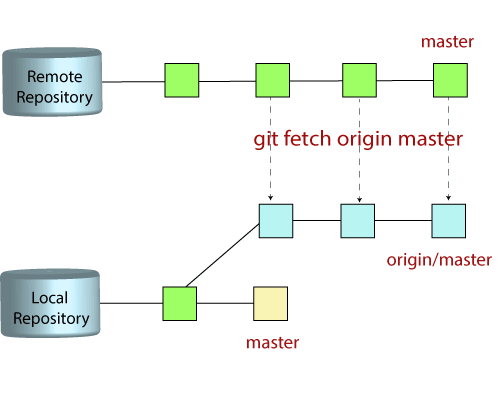
We need to navigate to a branch which contains all the changes that we need to merge with our fork repository.Open up Git bash and navigate to the working directory for this project on your local machine.Now, let's go through the steps which will help us to sync my fork repository with the original/upstream repository and get those changes. I have forked an open-source project called nopCommerce (F: 1).Īs you can see in the above image, my fork repository is 15 commits behind the original/upstream repository.
#GIT FETCH UPSTREAM HOW TO#
In this article, we will see how to merge original/upstream repository changes with our fork repository using Git.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
